查看全部菜单
전체메뉴
회사정보
회사소개
- 회사개요
- CEO인사말
- 연혁/수상
- 비전/조직문화
- 사업장
- CI
IR
- 경영정보
- 재무정보
- 주식정보
- IR자료실
- 공시
디지털 역사관
뉴스룸
- 보도자료
- 소셜미디어
- 홍보자료
LG Innotek Insights
제품정보
사업부개요
광학솔루션
- Camera Module
- 3D Sensing Module
- Optical Module
- Actuator
기판소재
- Package Substrate
- FC-BGA
- Display Solution
전장부품
- Connectivity Solution
- Autonomous Driving Solution
- Electrification Solution
- Lighting Solution
전자부품
- Power Solution
- Smart Home
ESG
ESG 경영
- CEO 메시지
- 비전/추진체계
- ESG 경영방침
Environment
- 탄소중립
- 자원순환
- 친환경 기술/제품
Social
- 구성원 자부심
- 안전/보건
- 공급망 ESG
- 사회공헌
- 사이버 신문고
Governance
- 경영투명성
- 주주 친화
- Risk Management
ESG Fact Book
- 지속가능성보고서
- 평가/인증
ESG활동
- 친환경 경영
- 사회책임 경영
- 신뢰받는 지배구조
- 외부수상
고객지원
FAQ
고객문의
소프트웨어라이브러리
News Letter 订阅申请
填写如下信息后申请,即可通过电子邮件接收 LG Innotek 的最新信息。
个人信息收集和使用协议(必填)
LG Innotek Co., Ltd.(以下简称“公司”)收集和使用的个人信息是根据“个人信息保护法”需要本人同意的信息。
1. 待处理的个人信息项目
[必填] 国家/姓名/电子邮件地址
[可选项目] 公司名称/电话号码
【自动收集的项目】服务使用记录(访问日期和时间)、访问IP信息
2. 处理和使用个人信息的目的
- 检查客户询问的事实
- 提供对客户查询和报告的答复或分配适当的人员
3. 个人信息的处理和保留期限
- 2个月
※ 您有权拒绝同意收集和使用个人信息,如果您不同意,可能会限制接收客户查询。
※ 14岁以下的儿童不能使用该服务.
同意向第三方提供个人信息(必填)
LG Innotek 向第三方提供以下个人信息以提供顺畅的服务。
1. 提供个人信息的人
LG Innotek Yantai Co., Ltd
LG Innotek Vietnam Haiphong Co., Ltd
LG Innotek Mexico S.A. de C.V.
LG Innotek Indonesia PT.
LG Innotek Poland Sp. z o.o
LG Innotek Taiwan Co., Ltd
LG Innotek Trading (Shanghai) Co., LTD.
LG Innotek Trading (Shanghai) Co.,LTD. Shenzhen Branch
LG Innotek Co.,Ltd. JAPAN (LGITJP)
LG Innotek USA
LG Innotek USA Inc. San Diego Office
LG Innotek USA Inc. Detroit Office
LG Innotek Co., Ltd. Europe Branch
2. 提供的个人信息项目
- 国籍/姓名/电子邮件/公司名称/电话号码
※ 公司名称和电话号码仅在提供时提供。
3. 处理和使用个人信息接收者的个人信息的目的
- 回答有关公司和产品等的咨询和其他服务
4. 接收个人信息的人保留和使用个人信息的期限
- 2个月
※ 您有权拒绝同意收集和使用个人信息,如果您不同意,可能会限制接收客户查询。
※ 14岁以下的儿童不能使用该服务
个人信息营销使用协议(可选)
LG Innotek Co., Ltd.(以下简称“公司”)收集和使用的个人信息是根据“个人信息保护法”需要本人同意的信息。
1. 待处理的个人信息项目
[必填项] 公司名称/姓名/E-mail/职位/职务
2. 处理和使用个人信息的目的
- 通过电话提供个人身份、时事通讯和活动电子邮件、产品信息和销售信息
- 营销活动,如营销活动、与产品和服务相关的沟通以及市场调查
3. 个人信息的处理和保留期限
- 直到撤回使用营销的同意
4. 个人信息委托状态
- 用于营销服务的个人信息处理委托给 Oracle Corporation、Golden Planet 和 Ipgdextra Korea。
※ 您有权拒绝同意收集和使用个人信息,如果您不同意,可能会限制提供定制的营销信息。
※ 14岁以下的儿童不能使用该服务
News Letter 订阅申请
填写如下信息后申请,即可通过电子邮件接收 LG Innotek 的最新信息。
News Letter 订阅申请
News Letter 订阅申请
LG Innotek Insights
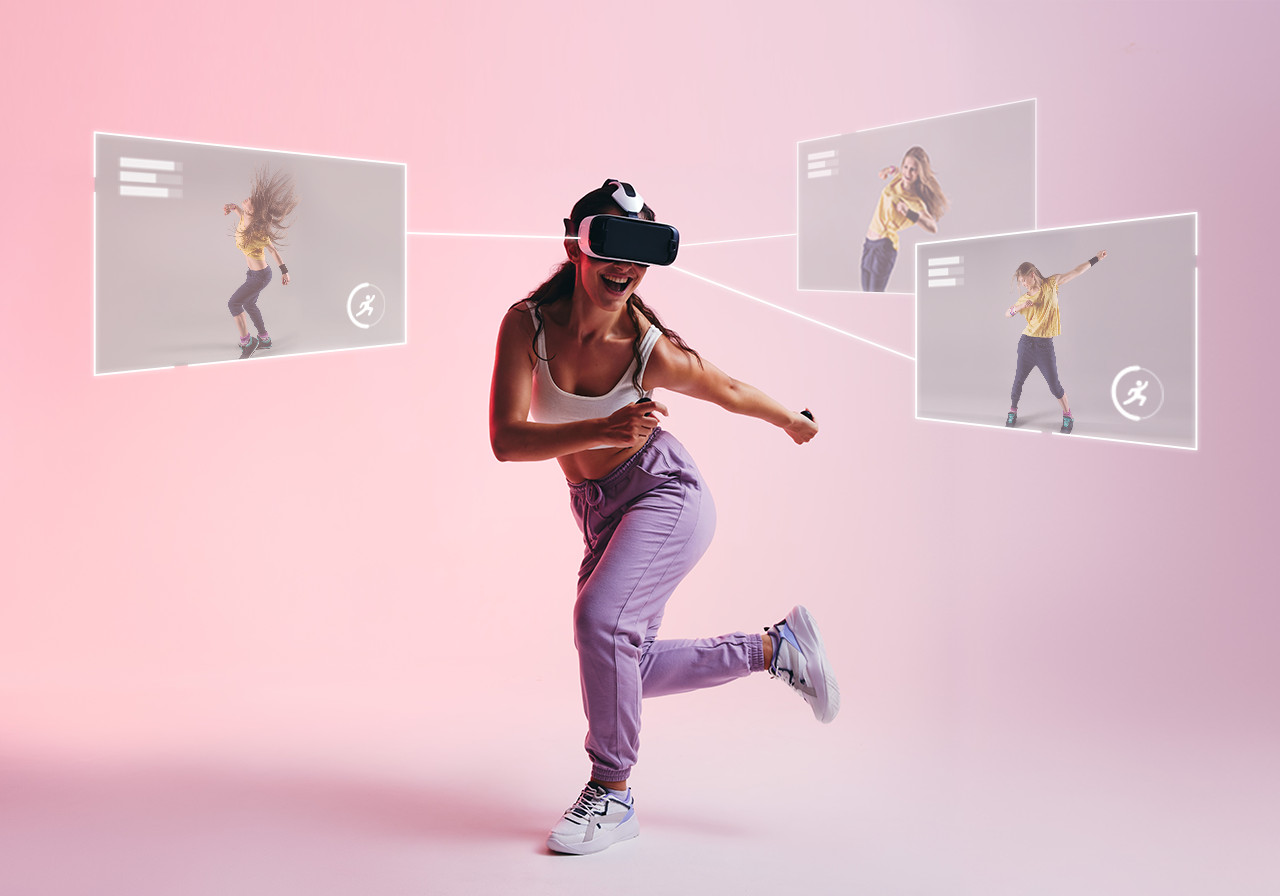


Due to the prolonged pandemic, our lives are restricted in many ways every day. At the same time, however, it’s also true that this situation has accelerated the growth of various new digital technologies. Even unfamiliar concepts such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and the metaverse are rapidly becoming part of our daily lives.
Take Emma, for example, who lives in Canada and is an avid K-pop fan. After learning K-pop cover dance moves through YouTube, she now wishes to take professional choreography lessons at a studio run by a popular dancer in Korea. As it’s difficult to visit Korea in person, what if there was an opportunity to participate in a class in the metaverse? With a camera that can recognize 3-dimensional information, Emma is one step closer to making her wish a reality.
If a smartphone camera equipped with 3D-sensing capabilities recognizes Emma’s dance movements from head to toe, then the teacher in Korea can provide feedback and coaching on his moves in real time. In addition, when Emma puts on the VR headset, she can virtually experience being in the class in Korea along with the choreography instructor and other students.
Then, there’s Oliver, who’s in charge of shipping at a logistics company. The development of metaverse technology will allow him to do his work faster and more efficiently. For instance, let’s say Oliver captures the delivered items with a 3D-sensing camera and transmits them to the company’s cloud. The central management system will then recognize the length, width, and volume of the packages and arrange for them to go to the on-site warehouse or put onto the delivery vehicles. This will help out Oliver greatly in terms of estimating the amount of space needed for loading, and figuring our shipping and delivery schedules.
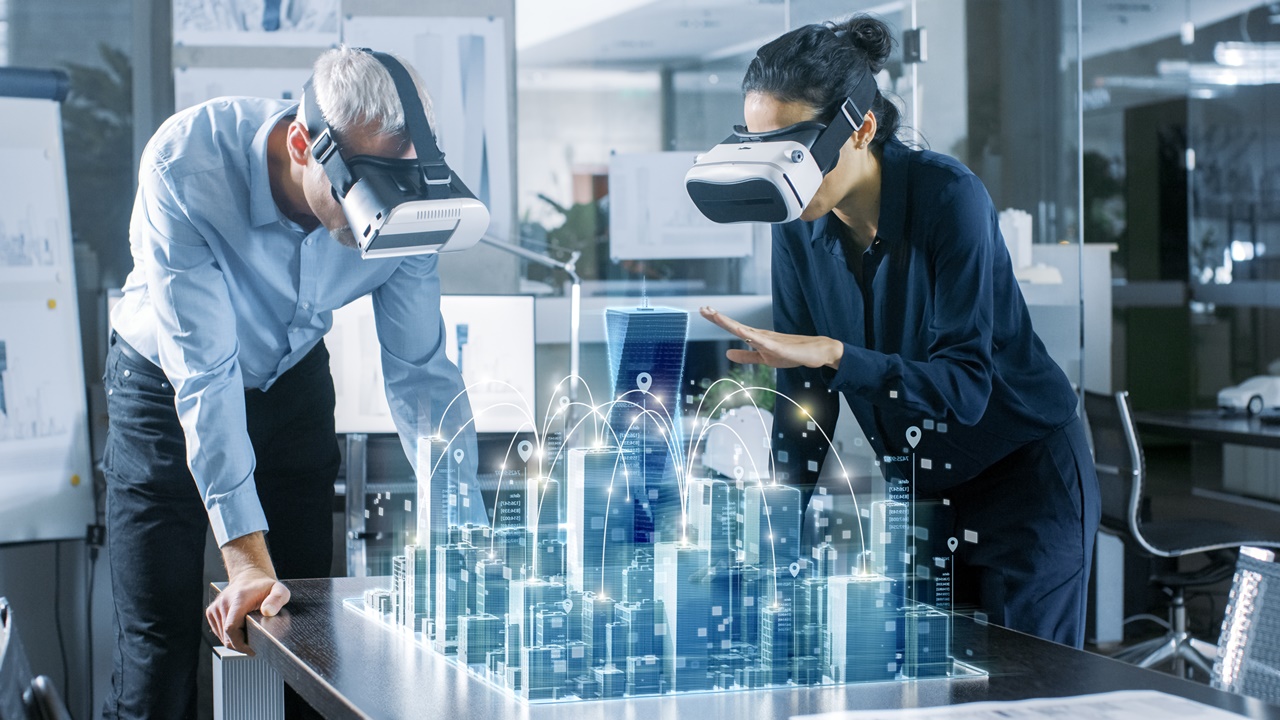

Like these scenarios above, the metaverse—in all its various capacities—is full of infinite possibilities, even beyond what we can imagine. Unlike the existing digital world where there are clear boundaries of reality and limited means of communication, the metaverse allowing for borderless connections and immersive experiences is a huge advantage. However, this sense of transcendence, due to the blurred boundary between the virtual and real, paradoxically stems from precise spatial mapping. Only by depicting reality in a truly tangible way can it blend naturally into the virtual space. If that’s the case, what kind of technology, which accurately recognizes real-life data, is needed to make the metaverse truly immersive?
ToF Module for 3D-Sensing - “Digital Eye” in the Metaverse era
As the above cases demonstrate, shaping accurate and realistic 3-dimensional environments is essential to making the metaverse a truly immersive platform. The demand for 3D-image-processing and image-sensing technologies is increasing steadily. According to Research and Markets, the global 3D-sensor market size is projected to grow from USD 2.9 billion in 2020 to USD 10.0 billion by 2025, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 27.9%.
The ToF (time of flight) module is crucial for 3D-sensing technology. It can render the virtual space within the metaverse in a manner almost identical to the real world. Considered the “eye” of the metaverse era, the ToF module recognizes real objects and makes them virtual, allowing 3D-sensing technology to mirror reality more authentically, heightening the metaverse experience.
ToF modules recognize 3-dimensionality, spatial information, and object movement by measuring the time it takes for light to bounce back of an object. Since the existing distance-estimation technology of the camera calculates the distance to an object based on a flat surface, current methods will have limitations in uneven places, and in dark environments. However, 3D-sensing based on ToF enables accurate 3D measurement as the module can detect the size and volume of irregular shapes such as circles and curved surfaces, derive absolute values rather than relative values, and is largely unaffected by ambient brightness.
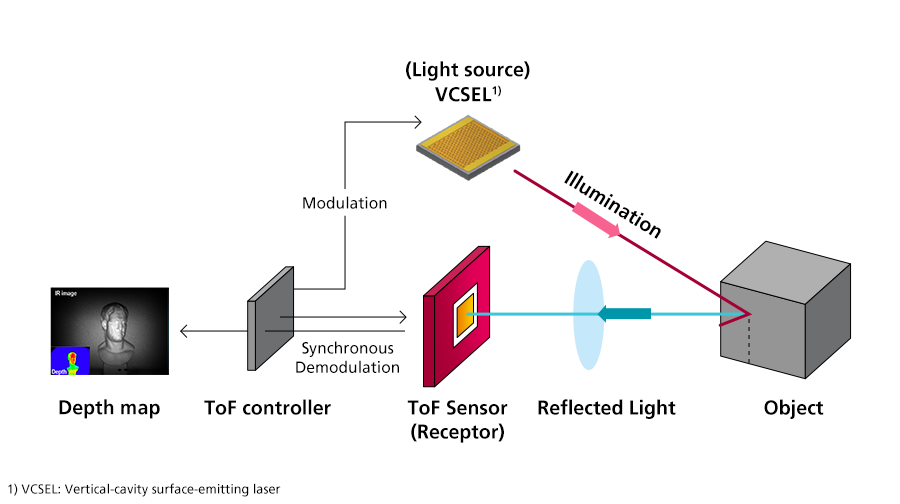
[The time-of-flight (ToF) principle] ToF is a method of measuring the distance between the sensor and the object based on the time difference between the emission of a signal (from the light source) and its return to the sensor, after being reflected by an object.
When a camera equipped with a ToF module is applied to a smartphone or wearable device, biometric authentication, motion recognition, AR and VR functions can be implemented. In addition, as metaverse-related killer apps appear, a new ecosystem for 3D-sensing cameras is created, and the utilization of the ToF camera module is expected to increase even further.
LG Innotek partners with Microsoft on Metaverse and the Cloud
In 2021, LG Innotek signed an MOU with Microsoft to cooperate in the development and supply of ToF modules, a 3D-camera component for Azure, with the mutual goal of bringing the product to market by August of this year. Azure, Microsoft's cloud platform, is a well-known solution, currently occupying approximately 20% of the global cloud market. LG Innotek plans to develop and mass-produce ToF modules for Azure together with Microsoft in addition to supplying the modules to Microsoft's global cloud customers.
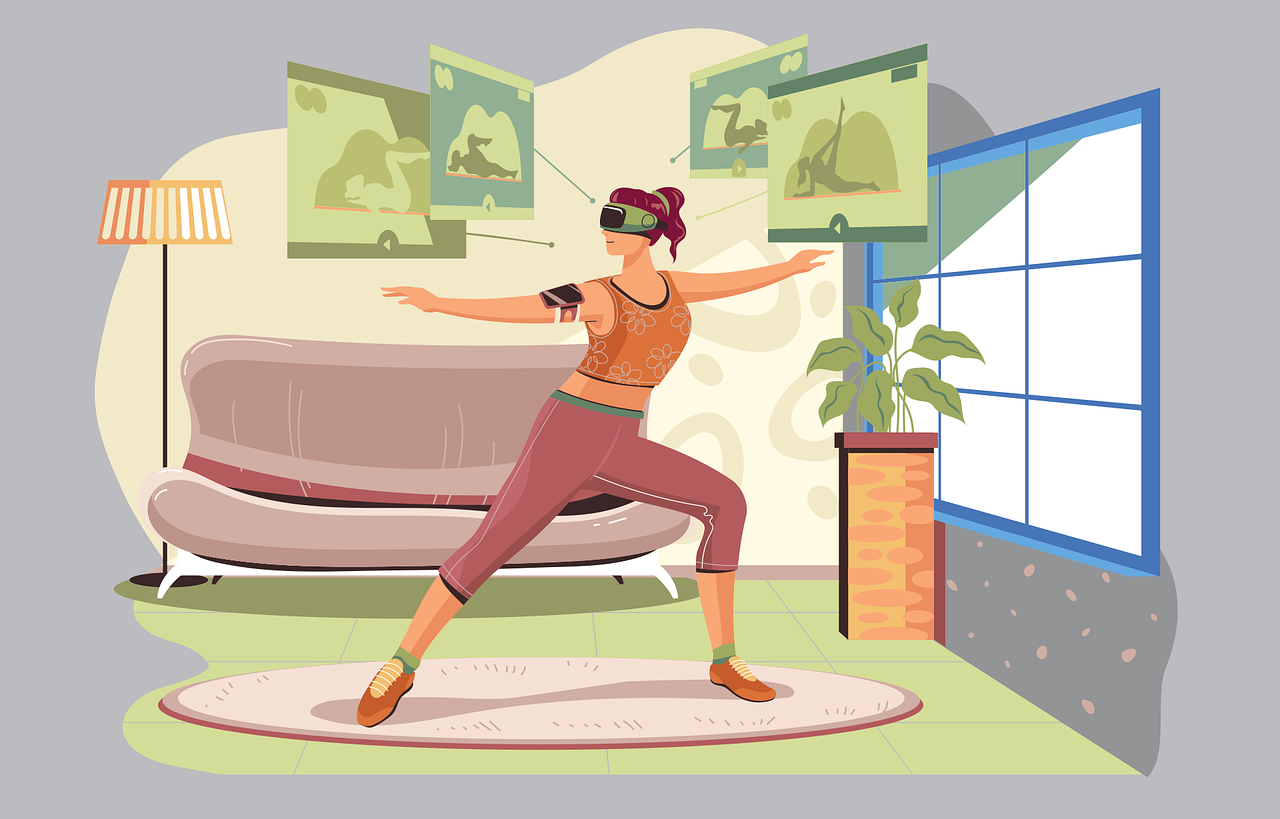

The technology has several applications across a long list of industries. For example, a fitness company can implement a ToF module in its wearable device and link it to the Azure cloud. The resulting product can provide fitness services combining AR/VR with detailed tracking of an individual’s movements. LG Innotek and Microsoft will also work together to grow the ToF-module customer base as this technology is expected to receive significant interest from fields such as global healthcare and distribution markets. Already participating in the B2B metaverse market, Microsoft is laying the groundwork for further expansion into B2C. The scope of cooperation between the two companies is expected to grow with this new foray into the B2C content-based metaverse market.
LG Innotek is a leader in the 3D-sensing market based on its world-class camera module technology and business know-how. In 2019, LG Innotek launched the 3D-sensing brand “InnoXensing,” leading the 3D sensing module market. “InnoXensing” is a combination of the words “innovation,” “X” (from “eXcellent,” “eXtream,” and “eXperience”), and “sensing” from 3D sensing. As the metaverse continues to evolve, LG Innotek will continue to support immersive experiences and inspiring customers with differentiated 3D-sensing technology.